In today’s industrial landscape, machinery is running faster, lighter, and with higher precision than ever before. High-speed applications—from robotics and aerospace systems to medical devices and automated production lines—place extreme demands on components. Thin section bearings, with their compact design and high load-carrying capacity relative to size, have emerged as a critical solution. However, selecting the right bearing is not just about picking a model off the shelf; it requires careful consideration of application needs, material properties, design, and supplier expertise.
How to Choose the Right Thin Section Bearing for High-Speed Applications
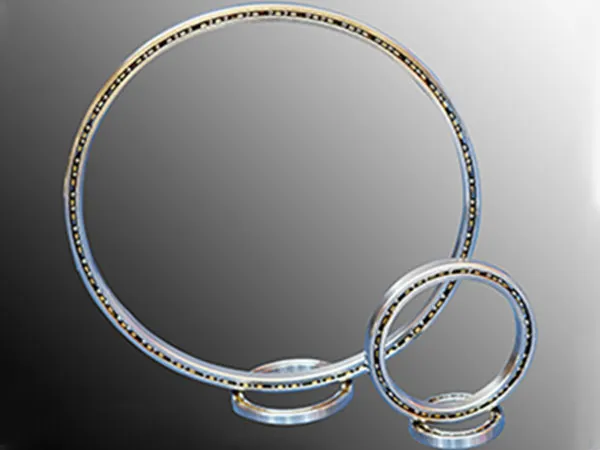

Here’s a comprehensive guide to help engineers, maintenance teams, and procurement specialists make informed choices that maximize performance and equipment longevity.
1. Define Your Application Requirements
Before choosing a bearing, it’s crucial to understand exactly what your machinery requires. High-speed operations impose unique stresses, and mismatched bearings can cause premature wear, vibration, or even catastrophic failure. Key factors to evaluate include:
Rotational Speed: Bearings must handle the maximum RPM with minimal friction. Excess friction generates heat, which can degrade lubrication and reduce bearing life.
Load Type and Magnitude: Determine whether your system applies radial, axial, or combined loads, and calculate the expected magnitude. Thin section bearings can handle high loads relative to size, but not all designs are equal.
Operating Environment: Temperature fluctuations, humidity, dust, chemical exposure, or cleanroom requirements affect material selection and lubrication strategies. Bearings exposed to corrosive chemicals or high temperatures need specialized coatings or materials.
By documenting these requirements upfront, you can narrow down options and avoid costly misapplications.
2. Understand Bearing Design and Dimensional Constraints
Thin section bearings come in several specialized designs, each suited for particular operational needs:
Crossed Roller Bearings: Excellent for high rigidity and precision under combined radial and axial loads. Ideal for robotic arms, turntables, and aerospace applications.
Angular Contact Bearings: Designed for high-speed rotation with moderate axial loads. Common in spindle assemblies and precision machinery.
Radial Ball Thin Section Bearings: Best for applications dominated by radial loads and moderate speeds, such as certain conveyor or indexing systems.
Additionally, consider physical dimensions carefully: the compact profile of thin section bearings is ideal for space-constrained designs, but the inner and outer diameters must integrate seamlessly into your assembly without interference. Misfit can lead to alignment issues or uneven load distribution.
…
For more detailed information on how to select the right thin-section bearings for high-speed applications, please click here: https://www.lynicebearings.com/a/blog/selection-of-thin-section-bearings-for-high-speed-applications.html